Reflection at Plane and Spherical Surfaces
Reflection at Plane and Spherical Surfaces: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Reflection of Light, Laws of Reflection of Light, Arrangement of Mirrors at a General Angle & 1/V versus 1/U Graph for Spherical Mirror etc.
Important Questions on Reflection at Plane and Spherical Surfaces
Which of the following bearings and their uses are correct?
In the figure shown consider the first reflection at the plane mirror and second at the convex mirror. AB is object
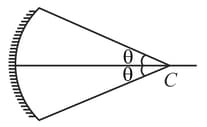
The circular boundary of the concave mirror subtends a cone of half angle at its centre of curvature. The minimum value of for which ray incident on this mirror parallel to the principle axis suffers reflection more than one is
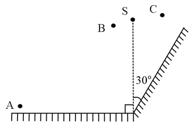
A point source of light is placed in front of two large mirrors as shown. Which of the following observers will see only one image of ?
A point source of light is 60 cm from a screen and is kept at the focus of a concave mirror which reflects light on the screen. The focal length of the mirror is 20 cm. The ratio of average intensities of the illumination on the screen when the mirror is present and when the mirror is removed is:
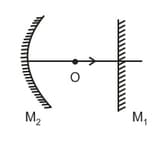
In the figure shown if the object 'O' moves towards the plane mirror, then the image I (which is formed after successive reflections from M1 & M2 respectively) will move:
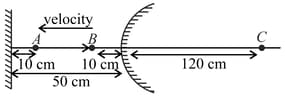
A luminous point object is moving along the principal axis of a concave mirror of focal length 12 cm towards it. When its distance from mirror is 20 cm its velocity is 4 cm/s. The velocity of the image in cm/s at that instant is:
An infinitely long rod lies along the axis of a concave mirror of focal length . The near end of the rod is at a distance from the mirror. Its image will have a length
An object is placed in front of a convex mirror at a distance of 50 cm. A plane mirror is introduced covering the lower half of the convex mirror. If the distance between the object and the plane mirror is 30 cm, it is found that there is no gap between the images formed by the two mirrors. The radius of the convex mirror is:
In the figure shown, the image of a real object is formed at point I. AB is the principal axis of the mirror. The mirror must be:

The reflection surface of a plane mirror is vertical. A particle is projected in a vertical plane which is also perpendicular to the mirror. The initial velocity of the particle is 10 m/s and the angle of projection is 60o. The point of projection is at a distance 5 m from the mirror. The particle moves towards the mirror. Just before the particle touches the mirror the velocity of approach of the particle and its image is:
There are two plane mirror with reflecting surfaces facing each other. The mirrors are moving with speed away from each other. A point object is placed between the mirrors. The velocity of the image will be
A man of height is walking away from a street lamp with a constant speed . The height of the street lamp is . The rate at which of the length of the man's shadow is increasing when he is at a distance from the base of the street lamp is:
A light ray is incident on a plane mirror . The mirror is rotated in the direction as shown in the figure by an arrow at frequency . The light reflected by the mirror is received on the wall at a distance from the axis of rotation. When the angle of incidence becomes find the speed of the spot (a point) on the wall?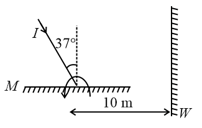
A large temple has a depression in one wall. On the floor plan, it appears as an indentation having a spherical shape of radius . A worshipper stands on the centreline of the depression, out from its deepest point, and whispers a prayer. Where is the sound concentrated after reflection from the black wall of the depression?
A thin road of length d/3 is placed along the principal axis of a concave mirror of focal length = d such that its image, which is real and elongated, just touches the rod. Find the length of the image?
Velocity of light is equal to:
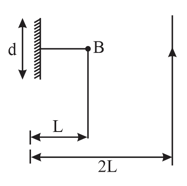
A point source of light placed at a distance in front of the centre of a mirror of width hung vertically on a wall. A man walks in front of the mirror along a line parallel to the mirror at a distance from it as shown in figure. The greatest distance over which he can see the image of the light source in the mirror is :
What is a point object in light?
What is the point object?
